Zero Trust Security solutions are rooted in a simple principle: no user, device, or application should be trusted by default, whether it originates inside or outside the network. For years, this model proved highly effective against conventional cyber threats. But the rapid evolution of artificial intelligence has changed the threat landscape.
While AI significantly boosts enterprise productivity and automation, it also opens new pathways for cyberattacks – forcing organizations to rethink traditional Zero Trust architectures.
AI has become both a powerful defender and a dangerous adversary. Cybercriminals now use AI to automate reconnaissance, craft highly personalized phishing campaigns, bypass authentication, and even manipulate security models. At the same time, AI enhances Zero Trust data protection by transforming static security controls into proactive, self-learning defenses. With AI-driven analytics, Zero Trust solutions can process massive volumes of data in real time, identify subtle anomalies, and predict potential breaches long before human analysts can even imagine.
In this blog, we will explore how AI is transforming modern Zero Trust solutions, outline key implementation strategies, discuss real-world use cases, address common challenges organizations face, and offer actionable insights to help strengthen cybersecurity posture.
What Is Zero Trust Cybersecurity?
Zero Trust cybersecurity is a modern security approach built on the philosophy that no entity, internal or external, should be assumed trustworthy at any point. Instead of relying on a secure network perimeter, Zero Trust data security assumes that every access attempt could be malicious and must be continuously validated. Every user, device, and application is authenticated, authorized, and monitored each time it requests access to any resource. Edge Computing Enhances Data Protection by decentralizing data processing closer to the source, which reduces latency and minimizes the risk of sensitive data being exposed during transmission. This further strengthens the Zero Trust model, providing an additional layer of security in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
According to Gartner, nearly two-thirds (63%) of organizations across the globe have already deployed zero-trust security models, either fully or in select parts of their infrastructure.
Core Pillars of Zero Trust

- Least Privilege Access- Access rights are minimized, ensuring users and devices only obtain the exact permissions required to perform their specific tasks, nothing more.
- Micro-Segmentation- The network is divided into smaller, isolated segments to prevent unauthorized lateral movement if an attacker gains access to one part of the system.
- Continuous Monitoring and Validation- All activities are evaluated in real time to quickly detect suspicious behavior and mitigate threats before they escalate.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)- Access is granted only after multiple verification checkpoints (such as password + biometrics or OTP), significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized entry.
Zero Trust Meets AI: The Ultimate Defense System
Artificial intelligence elevates Zero Trust from a rule-based security model to a dynamic, self-adapting defense system. By combining automation, contextual decision-making, and continuous learning, AI for Zero Trust systems allows security teams to detect threats earlier, respond faster, and reduce human dependency. Here’s how AI reinforces the Zero Trust framework:
Intelligent Threat Detection & Fast Response
Zero Trust and AI combinedly analyze enormous streams of network and user activity to uncover subtle indicators of risk that traditional tools often overlook.
- Anomaly Identification: Detects deviations from normal behavior, for example, a user suddenly accessing confidential files outside business hours.
- Predictive Analysis: Identifies potential threats based on recurring patterns and global cyberattack trends to stop breaches before they occur.
Deep Behavioral Analytics
Instead of relying solely on credentials, using AI for Zero Trust security frameworks validates identity by monitoring typical user and device patterns and flagging anything unusual.
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): Highlights actions like repeated failed login attempts or unauthorized downloads.
- Device Behavior Analytics: Alerts security teams to compromised devices by tracking inconsistent or suspicious system activity.
Autonomous Incident Containment
The integration of Zero Trust and AI reduces reaction time during cyber incidents by executing immediate protective actions.
- Blocking Malicious Sources: Suspicious IP addresses and traffic are automatically restricted.
- Quarantining Infected Systems: Potentially compromised endpoints are isolated to limit lateral movement inside the network.
Adaptive and Context-Aware Authentication
Authentication evolves in real time when using AI for Zero Trust security systems, based on the level of risk associated with each access attempt.
- Risk-Based Access: If a login occurs from an unusual location or device, additional identity checks are triggered to confirm legitimacy.
Real-Time Threat Intelligence
Zero Trust and AI together continuously aggregate and correlate threat insights from internal logs and global intelligence feeds to keep defenses aligned with emerging cyber risks.
Real-World Applications: How AI Is Powering Zero Trust in Action

Many global enterprises are already leveraging AI to take their Zero Trust strategies from theory to reality. The examples below highlight how AI-driven systems are strengthening identity validation, threat detection, and automated response, all core to a mature Zero Trust ecosystem.
Google – BeyondCorp
Google pioneered an AI-powered Zero Trust platform, BeyondCorp, which shifts security away from traditional perimeter defenses and toward identity- and device-centric validation.
- AI-based behavior analytics continuously evaluate user actions to detect anomalies such as unauthorized access attempts or abnormal data transfers.
- Impact: A significantly stronger security posture while enabling seamless remote access for employees, without relying on VPNs.
Palo Alto Networks – Cortex XDR
Cortex XDR by Palo Alto Networks integrates AI and machine learning across endpoints, networks, and cloud workloads for unified threat detection and response.
- Real-time AI monitors system activity to identify malware, lateral movement attempts, and suspicious traffic patterns.
- Impact: Faster threat discovery, reduced incident response time, and minimized breach risk across hybrid environments.
Darktrace – Autonomous Cyber AI
Darktrace, an independent cybersecurity platform, works with Zero Trust architectures and uses self-learning AI to understand the normal behavior of every digital asset within each organization.
- The system identifies deviations from established patterns and autonomously alerts or intervenes when a potential threat is detected.
- Impact: Adaptive, always-on defense against evolving threats, including those designed to bypass traditional security tools.
IBM Security – QRadar Advisor with Watson
IBM Security’s QRadar SIEM, powered by Watson AI, enhances threat investigation by correlating massive volumes of security telemetry.
- AI assists security teams by contextualizing incidents, prioritizing risks, and recommending next steps.
- Impact: Higher precision in threat detection and a more streamlined incident response process.
These real-world implementations show that AI is no longer optional in a Zero Trust strategy, but it is becoming the driving force behind its success. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, organizations that adopt AI for Zero Trust solutions gain a continuously improving, self-learning defense that stays ahead of attackers rather than reacting to them.
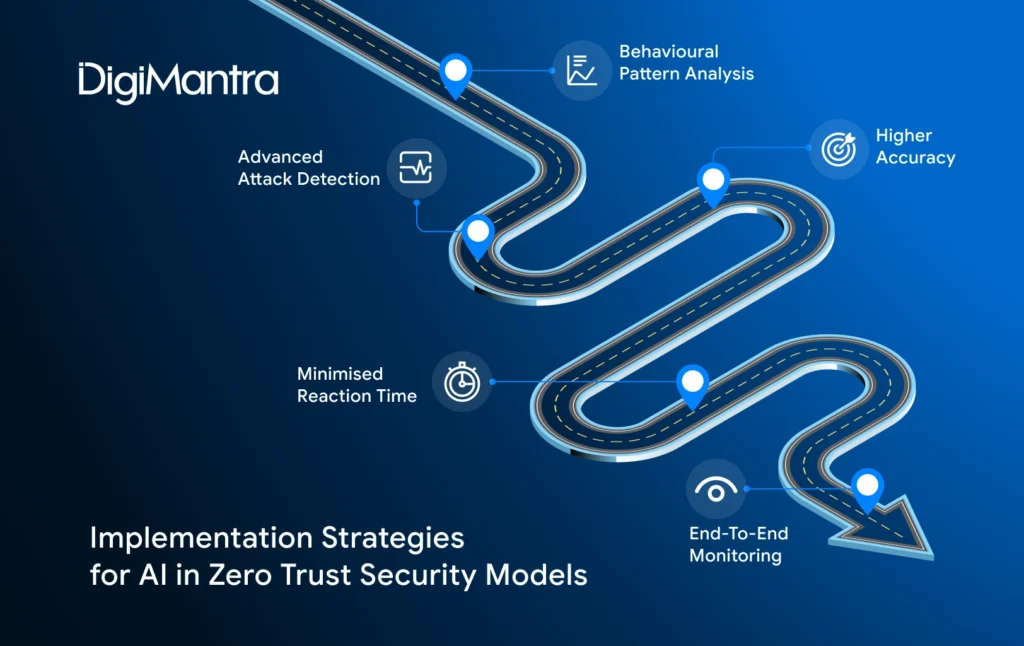
Implementation Strategies for AI in Zero Trust Security Models
AI brings the “dynamic decision-making” layer that Zero Trust has always needed. Traditional perimeter-based security reacts to threats after they surface, whereas AI enables a security system that anticipates, analyzes, and responds in real time.
When determining how to implement Zero Trust data protection, organizations should prioritize the following AI-driven strategies to unlock the full value of Zero Trust security solutions:
Use Machine Learning for Behavioral Pattern Analysis
Apply ML models that continuously evaluate user, device, and network behavior to detect subtle deviations that signal malicious intent. This shifts security from rule-based detection to intelligent, predictive threat identification, catching attacks that signatures and static policies would never spot.
Adopt Deep Learning for Advanced Attack Detection
Deep learning architectures can ingest massive datasets, from traffic logs to identity activity to autonomously learn what “normal” looks like across an environment. With every attempted attack, the Zero Trust data security becomes more discerning, making it highly effective against zero-day exploits and complex, multi-vector threats.
Integrate Metaheuristic Algorithms for Higher Accuracy
Pairing heuristic search techniques with learning models widens the exploration space during training, uncovering more accurate and optimized threat-detection pathways. This is crucial in cybersecurity, where attackers constantly adapt and no static model remains effective for long.
Automate Responses to Minimise Reaction Time
Configure AI systems not only to detect malicious activity but also to initiate countermeasures, such as isolating devices, revoking access, or blocking traffic, without human delay. This automated defense drastically reduces the time between detection and containment, preventing small breaches from escalating.
Enable Continuous, End-to-End Monitoring
Deploy AI tools that persistently inspect traffic, identities, workloads, applications, and endpoints. With generative AI-powered log interpretation, threat hunting becomes faster and more contextualized, supporting the Zero Trust principle of “never trust, continuously verify” at every layer of the ecosystem.
When implemented with a strategic approach, AI transforms Zero Trust security solutions from a static policy framework into a living, adaptive security model – one that predicts vulnerabilities, neutralizes threats in real time, and keeps the organization ahead of attackers instead of chasing them.
Challenges in Adopting AI-Driven Zero Trust Data Security
Although AI-powered Zero Trust has the potential to transform cybersecurity, the journey toward implementation is not without obstacles:
- Architectural Complexity- Zero Trust demands a fundamental redesign of legacy systems and network models, which can be time-intensive and technically demanding.
- High Upfront Investment- Advanced AI-based security platforms, automation tools, and expert resources can require substantial budget allocation, which may be challenging for SMEs.
- Privacy and Compliance Concerns- AI depends on extensive data access to learn and evaluate risks, raising questions about data governance, regulatory compliance, and responsible usage.
- Shortage of Skilled Talent- Many organizations lack trained professionals who understand both Zero Trust principles and AI-centric security operations.
- Risk of False Alerts- When not properly tuned, AI systems may misinterpret benign activity as malicious, resulting in alert fatigue and avoidable operational interruptions.
AI vs. Traditional Zero Trust Security Approaches
|
Feature |
Traditional Zero Trust |
AI-Powered Zero Trust |
| Access Control | Predefined rules and policies | Adaptive, behavior-based access |
| Authentication | One-time login verification | Continuous authentication using AI |
| Threat Detection | Manual monitoring & signature-based detection | Real-time AI-powered anomaly detection |
| Incident Response | Manual investigation and action | Automated response with machine learning |
| Micro-Segmentation | Static network segmentation | AI-driven dynamic segmentation |
| Threat Intelligence | Relies on past attack databases | Predictive threat analytics |
Final Thoughts
AI is transforming Zero Trust from a static framework into a living security ecosystem. With intelligent threat detection, automated mitigation, and continuous risk evaluation, using AI for Zero Trust solutions enables a security posture that adapts as fast as cyber threats evolve, closing the gaps traditional security leaves behind.
For security and technology leaders, the real objective isn’t just adopting AI but building a resilient defense strategy that aligns with business goals, scales with digital growth, and stays ahead of attackers. Success depends on the right mix of strategy, expertise, and execution, not just tools.
At DigiMantra, we help organizations build and deploy AI-enabled Zero Trust data security systems that don’t just react, they predict. Our machine learning and cybersecurity experts design security architectures that deliver measurable outcomes: stronger protection, lower operational overhead, and a competitive edge in the digital era.
Modern enterprises need security built on least-privilege access, continuous verification, and proactive threat prevention, rather than relying on perimeter trust or delayed remediation. With a human-first approach backed by advanced technology, our digital transformation company ensures your organization can protect what matters today while preparing for what’s next.
Build smarter security, not just stronger defenses. Let DigiMantra help you secure, scale, and lead with confidence.

AI-FIRST ENGINEERING FOR MODERN BUSINESSES
Designed for performance. Powered by innovation.
 Product Development
Product Development Custom Software
Custom Software Mobile & Web
Mobile & Web
 AI & Automation
AI & Automation Cloud Management
Cloud Management Intelligent Systems
Intelligent Systems