You’ve probably scrolled over them on social media: those amazing makeovers where ordinary photographs acquire a Miyazaki’s Ghibli look or where individuals are transformed into precisely detailed action figures, complete with that unmistakable plastic shine and tiny articulated joints.
This isn’t magic; it’s the power of advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning.
But how does it actually work? How does an AI, a collection? How does an AI, made of algorithms and data, learn to capture Ghibli’s charm or the toy’s look?
This blog will explore the technical mechanisms behind the transformations, focusing on the role of AI in creating Ghibli art and action figures.
The Core Challenges
The primary challenge in image transformation is not merely about changing colors or applying simplistic filters. The AI must perform several critical functions:
- Understand Content: The AI must accurately recognise the objects, people, and scenes in the input image. For instance, it should identify scenarios like “a person standing in a field” or “a cat sitting on a windowsill” with precision.
- Understand Style: The AI needs to firmly grasp the fundamental elements of the target aesthetic. In the case of Ghibli style, this means understanding characteristic linework, soft color palettes, and the specific ways clouds and foliage are rendered, in addition to key character design principles. When it comes to action figures, the AI must identify plastic textures, joint articulation, exaggerated features, base stands, and typical poses accurately.
- Apply Style Intelligently: The AI must merge the content of the original image with the learned style in a way that is both plausible and aesthetically consistent. This process is not just about overlaying; it involves a sophisticated reinterpretation of the content in the new style.
The Engine Room: Key AI Technologies
The primary challenge in image transformation is not merely about changing colors or applying simplistic filters. The AI must perform several critical functions:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
These are the primary tools for image processing. CNNs excel at handling grid-like data, like images. They employ layers of filters (kernels) to detect patterns, starting with basic edges and textures and advancing to recognize complex shapes, objects, and overall scene compositions. Feature extraction using CNNs is always the first, decisive step in image analysis.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
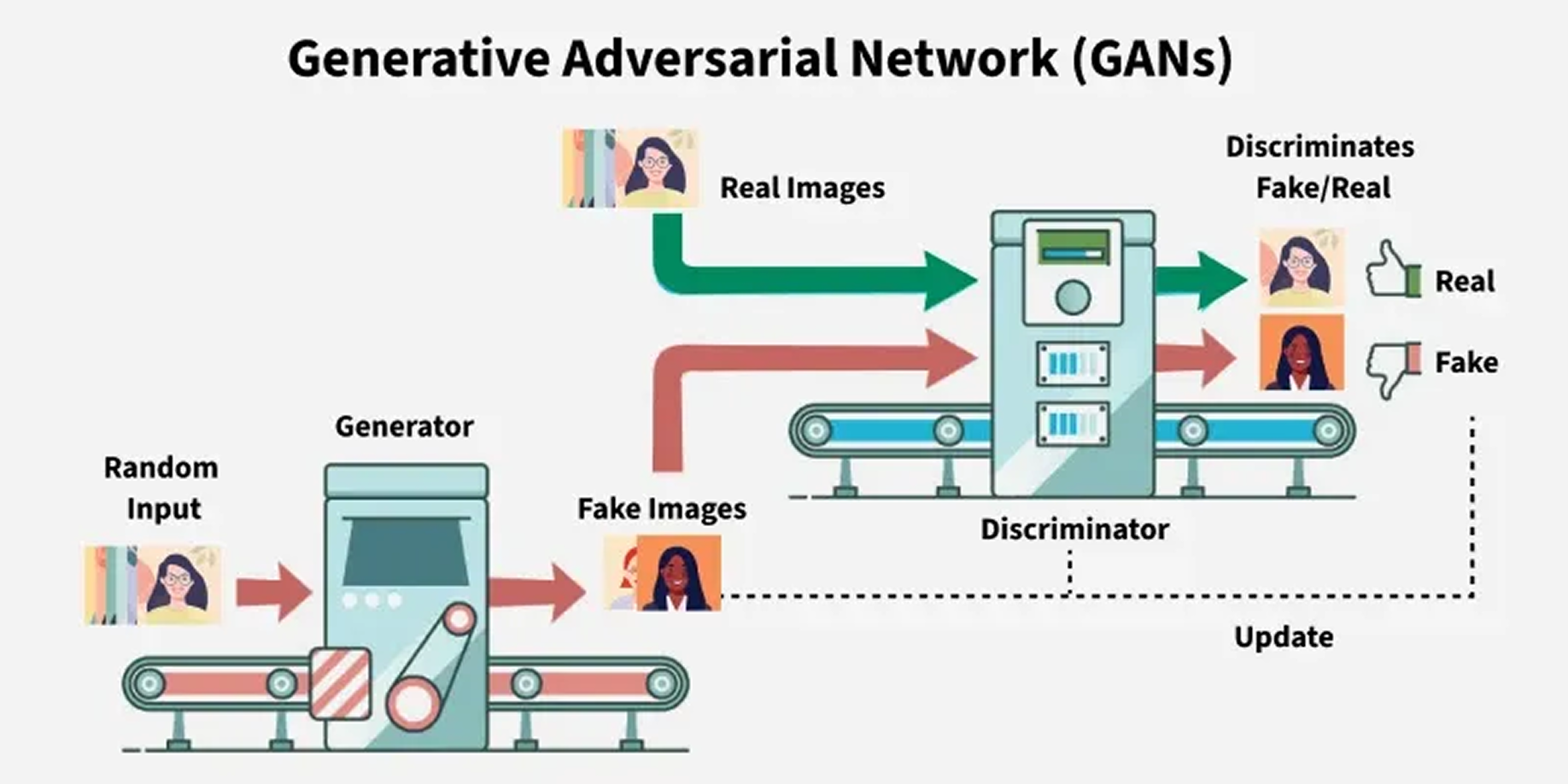
Imagine a fierce competition between two AIs: a Generator, intent on creating realistic images in the desired style, and a Discriminator, determined to differentiate between the Generator’s outputs and authentic examples of that style (e.g., genuine Ghibli stills or photographs of action figures). The process unfolds as follows:
- The Generator transforms noise or an input image into an intended style.
- The Discriminator evaluates both real images and the Generator’s output, refining its ability to classify them.
- The Generator leverages the Discriminator’s feedback to enhance its output continuously.
This adversarial framework enables the Generator to excel at producing images that closely align with the distribution of the target style. Specific GAN architectures, such as CycleGAN, are particularly adept at unpaired image-to-image translation, allowing for the transformation of photos into Ghibli style without requiring direct scene matches. StyleGAN is renowned for generating highly realistic and controllable images, often serving as the foundational model.
Diffusion Models
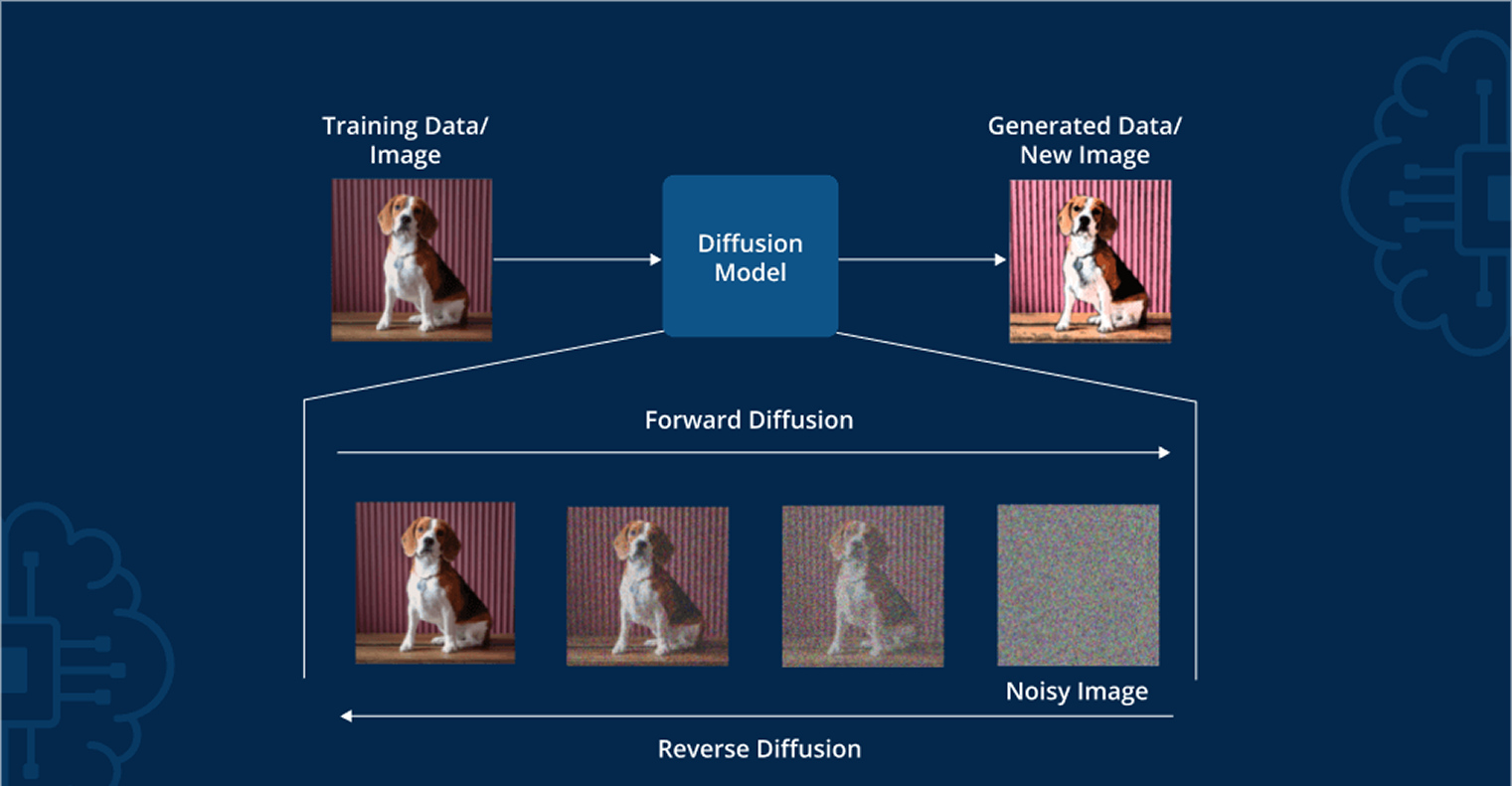
These models currently represent the pinnacle of high-fidelity image generation and manipulation. They work in two decisive stages
Forward Process (Noise Addition)
This begins with a real image, to which small amounts of Gaussian noise are methodically added until it becomes indistinguishable from pure static. The model skillfully learns the statistical structure of this noising process.
Reverse Process (Denoising/Generation)
This is where the true innovation lies. The AI learns to reverse the noise process, starting from pure noise and iteratively predicting and eliminating noise step by step, guided by specific conditioning information (like a text prompt or another image), until a clean and coherent image emerges. This meticulous iterative refinement allows for exceptional detail and adherence to prompts/styles. Models such as Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and DALL-E 2/3 heavily rely on these diffusion principles.
Transformers (especially Vision Transformers – ViTs)
Originally designed for natural language processing, Transformers are now making significant inroads into visual tasks. They systematically process images by breaking them into patches and discerning the relationships between these patches through self-attention mechanisms. This comprehensive understanding is crucial for tackling complex style applications and seamlessly integrating text prompts.
Mechanism 1: Transforming into Ghibli Style
This process undeniably falls within the boundaries of Neural Style Transfer (NST) and Image-to-Image Translation.
Early NST
These methods clearly separate content (the elements present in the image) from style (the manner of its rendering). They leverage a pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), such as VGG, to extract feature representations across different layers. Content is captured by deeper-layer features, while style emerges from the correlations between features in earlier and mid-layers, representing texture and patterns. An optimization process methodically adjusts the target image to align the content features of the input photo with the style features of the Ghibli reference image(s).
Limitation: This approach is characteristically slow, computationally intensive, and may produce artifacts. Moreover, it necessitates a specific style reference image.
GAN-based Approaches (e.g., CycleGAN, StyleGAN adaptations)
CycleGAN
This model effectively learns mappings between two domains, like photographs and Ghibli art, without requiring paired examples. It employs two Generators and two Discriminators. Generator A to B converts photos into Ghibli-style images, while Discriminator B evaluates their realism. Similarly, Generator B to A transforms Ghibli images back into photos, with Discriminator A assessing their authenticity. A critical “cycle consistency loss” ensures that when you transform an image from A to B and then back to A, you retrieve something closely resembling the original, preventing the model from producing random Ghibli images disconnected from the input photo. This method demands large datasets encompassing both photographs and Ghibli-style images.
StyleGAN-based Approaches
These methods can and should be fine-tuned on Ghibli datasets to generate images in that distinctive style. For transformation, techniques such as GAN inversion project the input photo into StyleGAN’s latent space, enabling manipulation of this latent code or the generator’s weights to apply the learned Ghibli style effectively.
Diffusion Model Approaches
These approaches are exceptionally effective and make use of an image-to-image (img2img) process. The input photo is intentionally noised during the forward diffusion process and then serves as a robust starting point for the reverse diffusion (denoising) process. Crucially, the denoising is conditioned on the desired style. This conditioning can emerge from:
A Text Prompt
For instance, “A photo of [original image content], in the style of Studio Ghibli, detailed anime, soft colors, hand-drawn look.” The model capitalizes on its understanding of “Studio Ghibli,” drawn from extensive training data that includes tagged Ghibli images, steering the denoising towards that aesthetic.
Model Fine-tuning
By training a base diffusion model specifically on Ghibli artwork, utilizing techniques like LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) or Dreambooth, it inherently generates outputs in that style and responds more robustly to Ghibli-related prompts.
ControlNets
These provide decisive control by accommodating additional conditioning inputs, such as edge maps or depth maps derived from the original image, ensuring the output structure closely adheres to the input while simultaneously transforming the style.
Mechanism 2: Generating AI Action Figures
Imagine a world where your favourite characters and personalities come to life as action figures crafted with precision and artistry through advanced generative models. This innovative process harnesses cutting-edge technology to masterfully understand 3D forms, textures, and object properties – all guided by carefully constructed text prompts.
GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
These powerful tools can be trained on extensive datasets of action figure images. By providing a conditional GAN with an input image (for example, a person’s face) and a prompt like “action figure,” we can generate striking results. However, achieving consistent details such as articulated joints and authentic plastic textures remains a challenge worth tackling.
Diffusion Models (Dominant Approach)
Enter models like Stable Diffusion and Midjourney, which excel at blending text and image conditioning. Their ability to produce compelling visual content opens up endless possibilities for creating lifelike action figures.
Text-to-Image (with Image Input Influence)
To create your ideal action figure, simply supply a detailed text prompt alongside an input image. For instance: “Action figure of [person/character description from image], highly detailed, plastic toy, articulated joints, standing on a display base, cinematic lighting, octane render.” The results will truly shine.
Image-to-Image
Utilizing the input image as a structural base, this process expertly denoises the initial, rough version. Guided by the “action figure” prompt, the AI reinterprets skin as plastic, incorporates joint lines, and adjusts proportions to evoke a toy-like essence. It may also generate a captivating display base to enhance the final product.
Understanding “Action Figure”
The magic lies in the model’s training data. It has processed countless images tagged with “action figure,” “toy,” “plastic,” and “articulated.” The model learns valuable statistical correlations – like the association of shiny plastic sheen with action figures, visible seam lines for joints, specific proportions, and often a display base, branded or plain. Your input prompt taps into these learned associations to create something extraordinary.
ControlNets and IP-Adapters
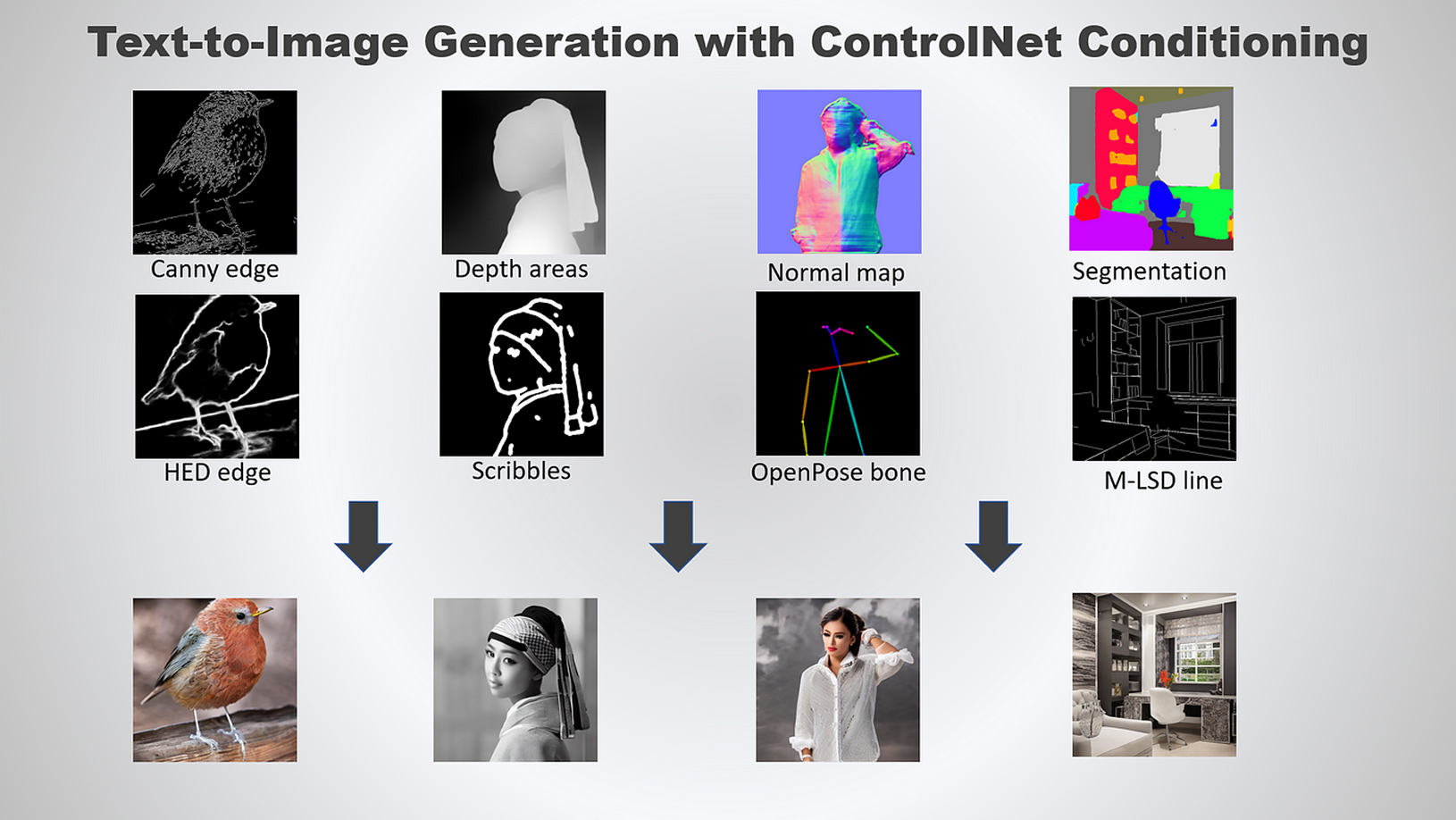
These advanced tools are game-changers. ControlNet utilizes depth maps, pose information, or canny edges from the input image, ensuring each generated action figure captures the pose and essence of the original subject perfectly. Meanwhile, IP-Adapters (Image Prompts) allow the model to closely adhere to the visual style of any reference action figure images provided. Embrace the future of action figure creation!
The Step-by-Step Conversion Process (Simplified)
- Input: Users begin by uploading an image. A text prompt can also be added to achieve more tailored results, especially for action figures or the enchanting Ghibli style.
- Preprocessing: The uploaded image undergoes resizing, normalization (adjusting pixel values to a standard range), and potentially an initial feature analysis to prepare valuable conditioning data, such as edge maps utilized by ControlNet.
- Encoding/Feature Extraction: In this stage, the image is channelled through the early layers of a neural network – typically a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) or the encoder part of a diffusion model/Visual Transformer (ViT) – to glean essential content features. For specific models, like StyleGAN, the image may be “inverted” into the model’s latent space for deeper analysis.
- Transformation/Generation (The Core):
- Style Transfer (GAN/NST): The image’s core features are manipulated or blended with stylistic elements, allowing the generator network to synthesize a compelling output image.
- Diffusion (img2img): Here, the input image (often slightly noised) and any corresponding text prompt guide a sophisticated denoising process. The model diligently refines a noisy canvas, utilizing the input image’s structure along with the stylistic directives from the prompt (like “Ghibli,” “action figure,” or “plastic toy”), meticulously eliminating noise to achieve the envisioned aesthetic.
- Decoding/Post-processing: This stage converts The internal representation back into a pixel-based image. Optional enhancements, such as AI upscaling (to boost resolution) or minor artefact corrections, may also be applied to ensure top-quality output.
- Output: Finally, users receive the beautifully transformed image, ready to impress.
This entire process hinges on access to vast quantities of high-quality, relevant data:
- For Ghibli: The AI must be trained using thousands (if not millions) of images, including many actual film stills and related artwork, meticulously curated to reflect the “Ghibli style.”
- For Action Figures: A successful model requires countless photos of diverse action figures, accurately tagged, to enable the AI to learn and replicate the common visual characteristics.
The richness and quality of this data fundamentally impact the model’s ability to generalize and deliver strikingly realistic results across various inputs.
Challenges and the Future
- Consistency: Achieving flawless stylistic consistency within complex scenes remains a significant challenge.
- Artifacts: Occasionally, generated images might display peculiar distortions or unnatural elements.
- Control: Despite significant advancements (notably with Diffusion and ControlNets), achieving precise control over every aspect of the output style is still an ongoing research challenge.
- Identity Preservation: Maintaining a strong resemblance of the transformed subject to the original while adopting a new style can be tricky; developers often face a tough trade-off between style fidelity and content integrity.
- Computational Cost: The training and operation of these large models necessitate considerable computing resources (GPUs/TPUs).
As we look forward, the future promises even more advanced models that will provide superior control, accelerated generation, and enhanced fidelity, possibly incorporating few-shot learning where the AI can master styles from limited examples. Furthermore, we anticipate tighter integration with 3D comprehension, facilitating more accurate transformations, especially for items like action figures.
Conclusion

Transforming images into captivating Ghibli art or AI-crafted action figures is a remarkable testament to the capabilities of deep learning, predominantly through generative models like GANs and Diffusion Models. These sophisticated systems learn intricate patterns and relationships through extensive datasets, enabling them to masterfully separate and recombine image content and style or reinterpret subjects based on specific textual prompts. This complicated process represents a symphony of feature extraction, adversarial training or iterative denoising, and precise conditioning, all driven by the extraordinary capacity of neural networks to comprehend and generate visual data. This “magic” may seem complex but is fundamentally rooted in rigorous mathematics, high-quality data, and innovative algorithmic design.
As the demand for AI-assisted creativity continues to rise, partnering with a digital transformation company can empower artists, collectors, and brands to blend imaginative Ghibli-style artistry with cutting-edge technology, opening the door to limitless possibilities in future character and action-figure design.

AI-FIRST ENGINEERING FOR MODERN BUSINESSES
Designed for performance. Powered by innovation.
 Product Development
Product Development Custom Software
Custom Software Mobile & Web
Mobile & Web
 AI & Automation
AI & Automation Cloud Management
Cloud Management Intelligent Systems
Intelligent Systems